Choosing controls and subsequently optimizing the allocation of resources to risk controls requires identification and processing the many to many relationships involved between risk events, causes of the events, and objectives to which the events have consequences.
Because a control to reduce the likelihood of a source can also reduce the likelihood of other sources, there is a many to many relationship between controls and sources, which can lead to economies as the resources expended for a control for one source can also reduce the likelihood of other sources and these sources can be causes of many events.
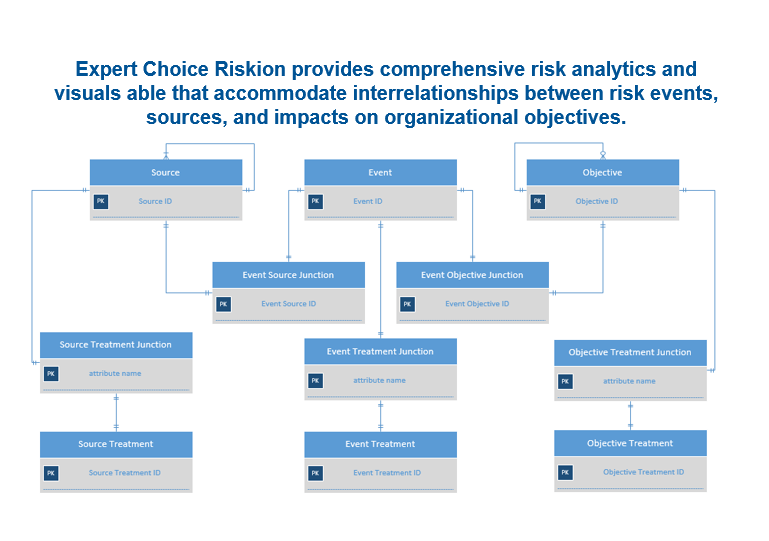 Similarly there is a many to many relationship between controls to reduce the likelihood of an event from a given source and the event with other sources as well as a many to many relationship between controls to reduce the likelihood of other events with other sources.
Similarly there is a many to many relationship between controls to reduce the likelihood of an event from a given source and the event with other sources as well as a many to many relationship between controls to reduce the likelihood of other events with other sources.
Finally, each event can have consequences to several objectives and each objective can have consequences from several events.
A spreadsheet is incapable of modelling or calculating many-to-many risk relationships.
These relationships and the ratio scale estimates of likelihoods and consequences must be addressed in a systematic fashion and maintained in a relational database with user interfaces such as series of ‘bow tie’ diagrams. For that, you need software that models the inter-relationships, and is capable of converting existing data and judgments to ratio scale measures that can be combined, based on sound math and risk measurement principles.
Want to learn more about how Riskion handles many-to-many elements for accurate risk assessments? Subscribe to our blog, or sign-up for our on-demand webinar.